
Category: TOPOCHEMICAL ENGINEERING


Novel cationic cellulose beads for oral delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs
Cellulose beads emerge as carriers for poorly water-soluble drugs due to their eco-friendly raw materials and favorable porous structure. However, drug dissolution may be limited by their poor swelling ability and the...

Topochemical Design of Cellulose-Based Carriers for Immobilization of Endoxylanase
Xylooligosaccharides (XOSs) gained much attention for their use in food and animal feed, attributed to their prebiotic function. These short-chained carbohydrates can be enzymatically produced from xylan, one of the most prevalent...

Fabrication of cellulose cryogel beads via room temperature dissolution in onium hydroxides
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in green solvents to dissolve and shape cellulose into microspheres. However, development of solvents suitable for room temperature dissolution and shaping of cellulose...

Cellulose Valorization for the Development of Bio-Based Functional Materials via Topochemical Engineering – Sustainability of Biomass through Bio-based Chemistry, 2021
Bio-based natural resources are of significant scientific importance in this era due to their rich existence, renewability, easy accessibility, low cost, etc. Cellulose, the naturally occurring biopolymer abundant in plants and woods...
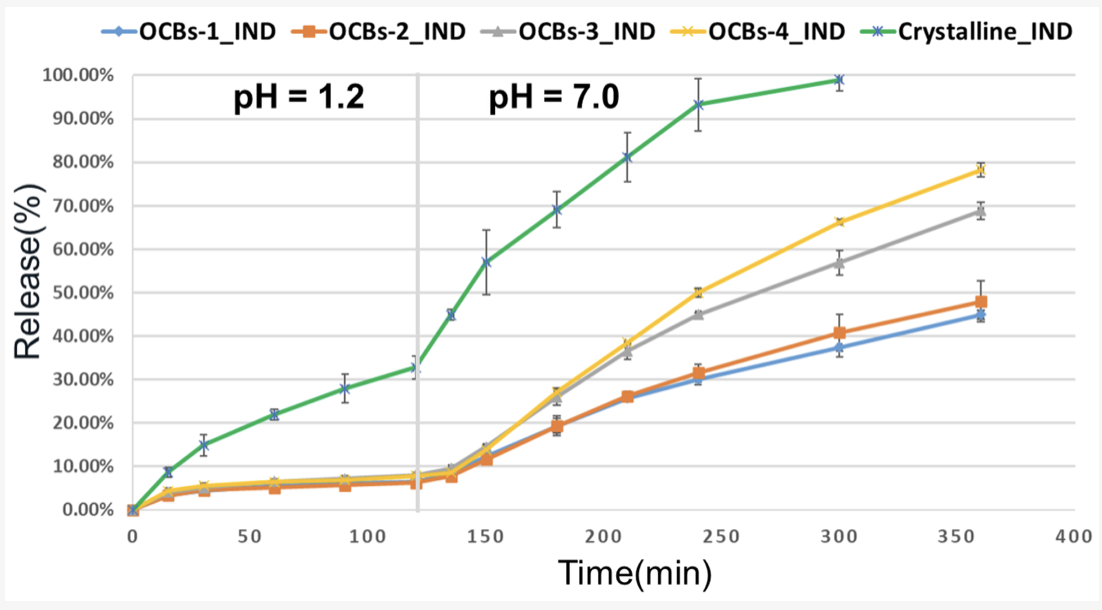
TEMPO-oxidized cellulose beads as potential pH-responsive carriers for site-specific drug delivery in the gastrointestinal tract
The development of controlled drug delivery systems based on bio-renewable materials is an emerging strategy. In this work, a controlled drug delivery system based on mesoporous oxidized cellulose beads (OCBs) was successfully...

In vitro and in vivo evaluation of poly-3-hydroxybutyric acid-sodium alginate as a core-shell nanofibrous matrix with arginine and bacitracin-nanoclay complex for dermal reconstruction of excision wound
The protective layer of the body, the skin is often prone to damage due to several factors like trauma, accidents, stress and hazardous exposure. This requires the skin to regenerate itself which...

Topochemical Engineering of Cellulose—Carboxymethyl Cellulose Beads: A Low-Field NMR Relaxometry Study
The demand for more ecological, highly engineered hydrogel beads is driven by a multitude of applications such as enzyme immobilization, tissue engineering and superabsorbent materials. Despite great interest in hydrogel fabrication and...
