
Category: TOPOCHEMICAL FABRICATION


In vitro and in vivo evaluation of poly-3-hydroxybutyric acid-sodium alginate as a core-shell nanofibrous matrix with arginine and bacitracin-nanoclay complex for dermal reconstruction of excision wound
The protective layer of the body, the skin is often prone to damage due to several factors like trauma, accidents, stress and hazardous exposure. This requires the skin to regenerate itself which...

Patterned dextran ester films as a tailorable cell culture platform
The elucidation of cell-surface interactions and the development of model platforms to help uncover their underlying mechanisms remains vital to the design of effective biomaterials. To this end, dextran palmitates with varying...

Fabrication of Biohybrid Polysaccharide-Protein Material for Wound-Healing Application
Tissue engineering is currently one the fastest growing engineering fields, requiring fabrication of advanced and multifunctional materials to be used as scaffolds or dressing for tissue regeneration. In this work, a bilayer...
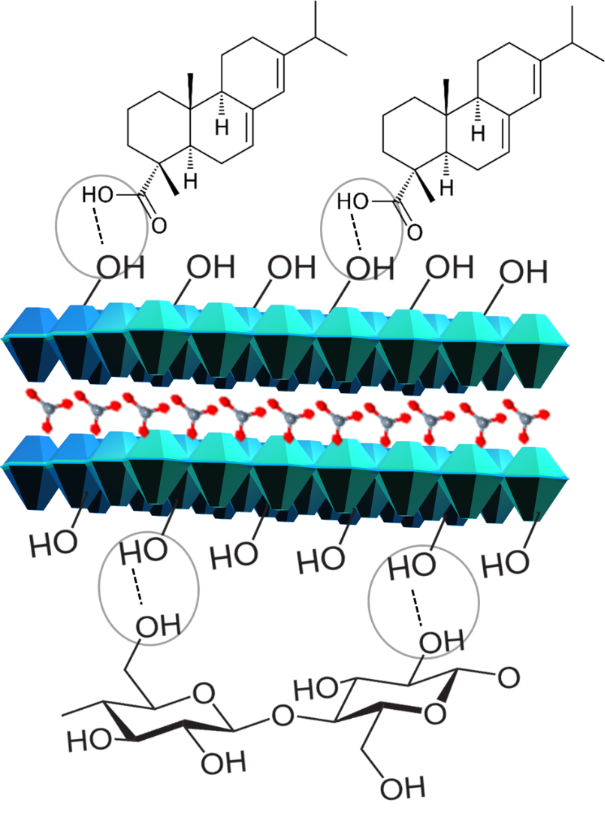
Topochemical engineering of composite hybrid fibers using layered double hydroxides and abietic acid
Topochemical engineering of hybrid materials is an efficient way of synthesizing hydrophobic and highly tensile fiber composites by utilizing the intermolecular hydrogen bonds in natural materials. These materials include wood pulp fibers,...
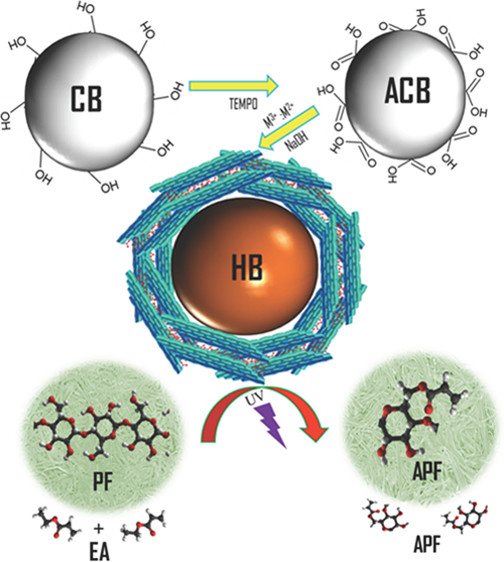
A Novel Catalyst: Biohybrid cellulose beads
Cellulose-based materials are very attractive for emerging bioeconomy as they are renewable, inexpensive, and environmentally friendly. Cellulose beads are spherical and porous and can be highly engineered to be used as catalyst...

Polysaccharides for tissue engineering
Biological studies on the importance of carbohydrate moieties in tissue engineering have incited a growing interest in the application of polysaccharides as scaffolds over the past two decades. This review provides a...

Multifunctional hydrogel beads for tissue engineering
Cytocompatible polysaccharide-based functional scaffolds are potential extracellular matrix candidates for soft and hard tissue engineering. This paper describes a facile approach to design cytocompatible, non-toxic, and multifunctional chitosan-cellulose based hydrogel beads utilising...
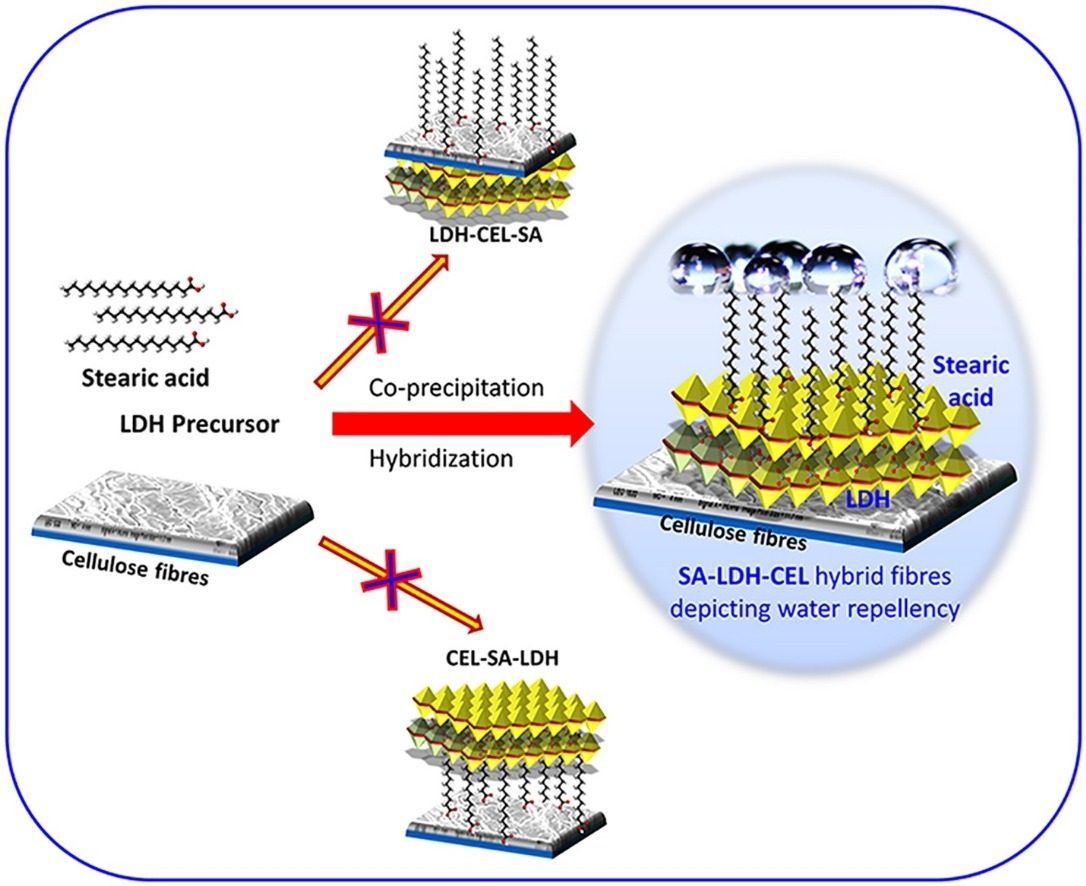
A new class of superhydrophobic hybrid materials
Technical composite materials derived from renewable sources are always of high importance due to cost-effectiveness and environmental concern. Cellulose, a renewable biopolymer stays constantly at the high realm in terms of valorization...
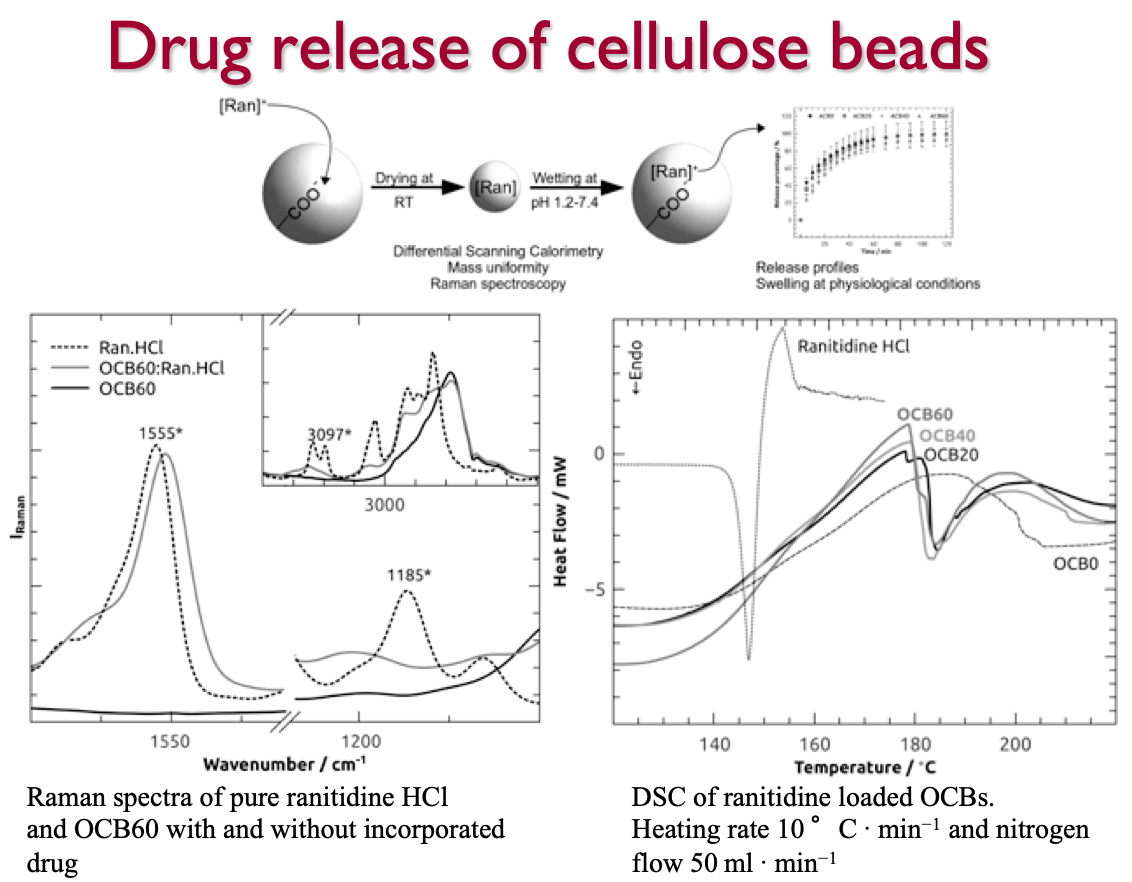
Solid‐state properties and controlled release of ranitidine hydrochloride
Oxidised cellulose beads (anionic groups 0.1–1.85 mmol g−1) were loaded with ranitidine HCl. Polymorphic form and crystallinity of the drug was assessed by calorimetric and spectrometric techniques. Release profiles were obtained at physiological conditions...